Data Structures | |
| class | BuildTest |
| class | InvalidUriException |
| Invalid Uri. More... | |
| class | NormalizeTest |
| class | ParseTest |
| class | ResolveTest |
| class | SplitTest |
| class | Version |
| This class contains the version number for this package. More... | |
Functions | |
| resolve ($basePath, $newPath) | |
| This file contains all the uri handling functions. More... | |
| normalize ($uri) | |
| Takes a URI or partial URI as its argument, and normalizes it. More... | |
| parse ($uri) | |
| Parses a URI and returns its individual components. More... | |
| build (array $parts) | |
| This function takes the components returned from PHP's parse_url, and uses it to generate a new uri. More... | |
| split ($path) | |
| Returns the 'dirname' and 'basename' for a path. More... | |
| _parse_fallback ($uri) | |
| This function is another implementation of parse_url, except this one is fully written in PHP. More... | |
Function Documentation
◆ _parse_fallback()
| Sabre\Uri\_parse_fallback | ( | $uri | ) |
This function is another implementation of parse_url, except this one is fully written in PHP.
The reason is that the PHP bug team is not willing to admit that there are bugs in the parse_url implementation.
This function is only called if the main parse method fails. It's pretty crude and probably slow, so the original parse_url is usually preferred.
- Parameters
-
string $uri
- Returns
- array
Definition at line 302 of file functions.php.
References $result.
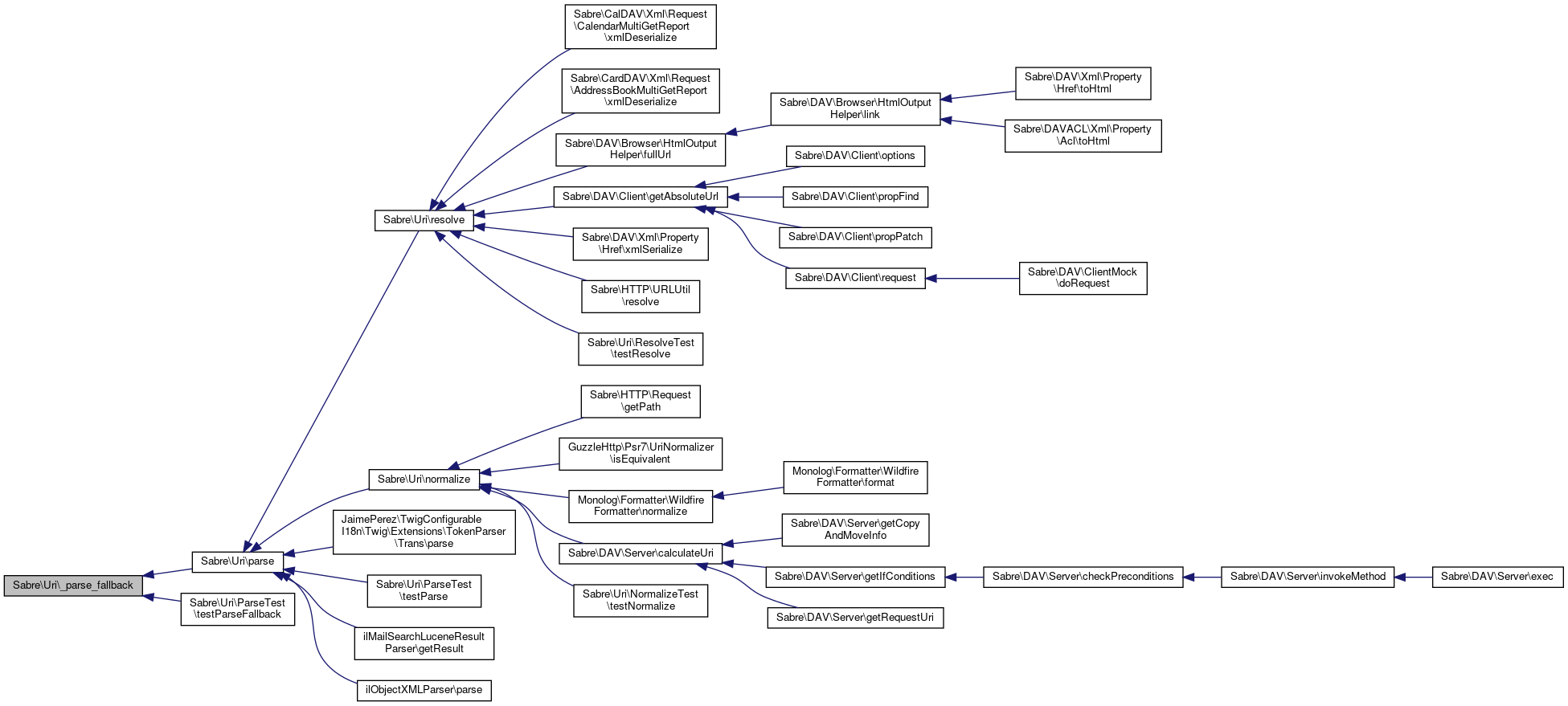
Referenced by Sabre\Uri\parse(), and Sabre\Uri\ParseTest\testParseFallback().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ build()
| Sabre\Uri\build | ( | array | $parts | ) |
This function takes the components returned from PHP's parse_url, and uses it to generate a new uri.
- Parameters
-
array $parts
- Returns
- string
Definition at line 221 of file functions.php.
References $authority.
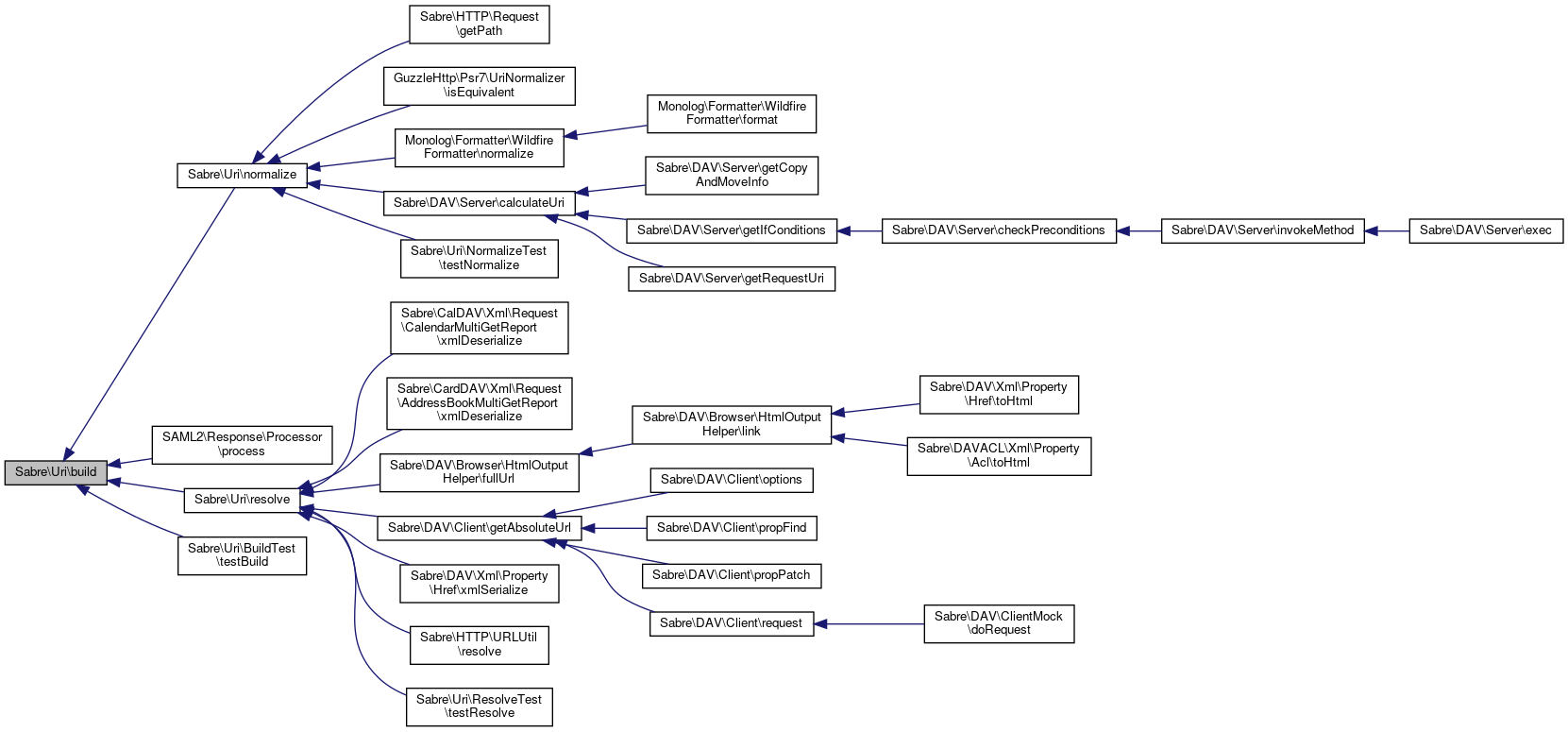
Referenced by Sabre\Uri\normalize(), Sabre\Uri\resolve(), and Sabre\Uri\BuildTest\testBuild().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ normalize()
| Sabre\Uri\normalize | ( | $uri | ) |
Takes a URI or partial URI as its argument, and normalizes it.
After normalizing a URI, you can safely compare it to other URIs. This function will for instance convert a %7E into a tilde, according to rfc3986.
It will also change a %3a into a %3A.
- Parameters
-
string $uri
- Returns
- string
Definition at line 114 of file functions.php.
References Sabre\Uri\build(), and Sabre\Uri\parse().
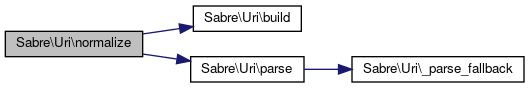
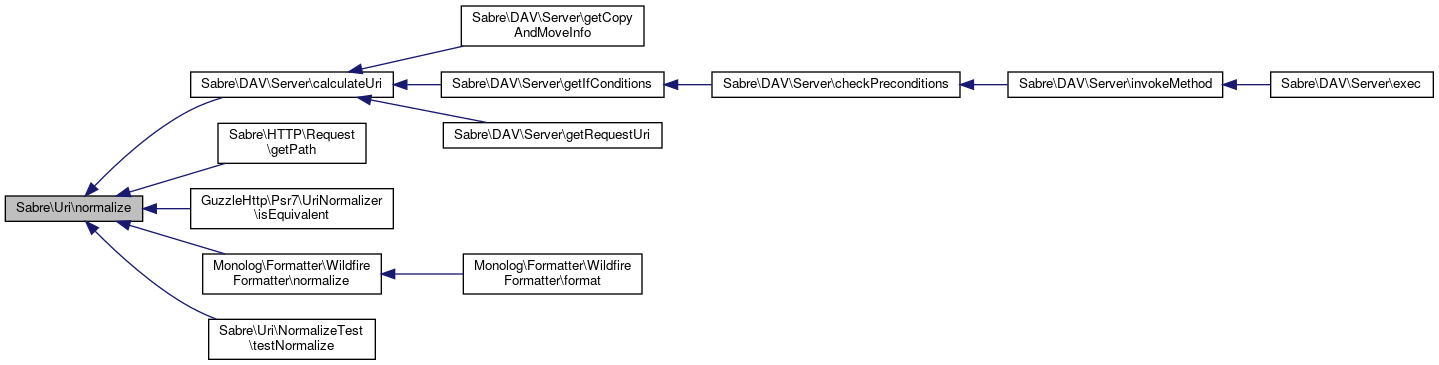
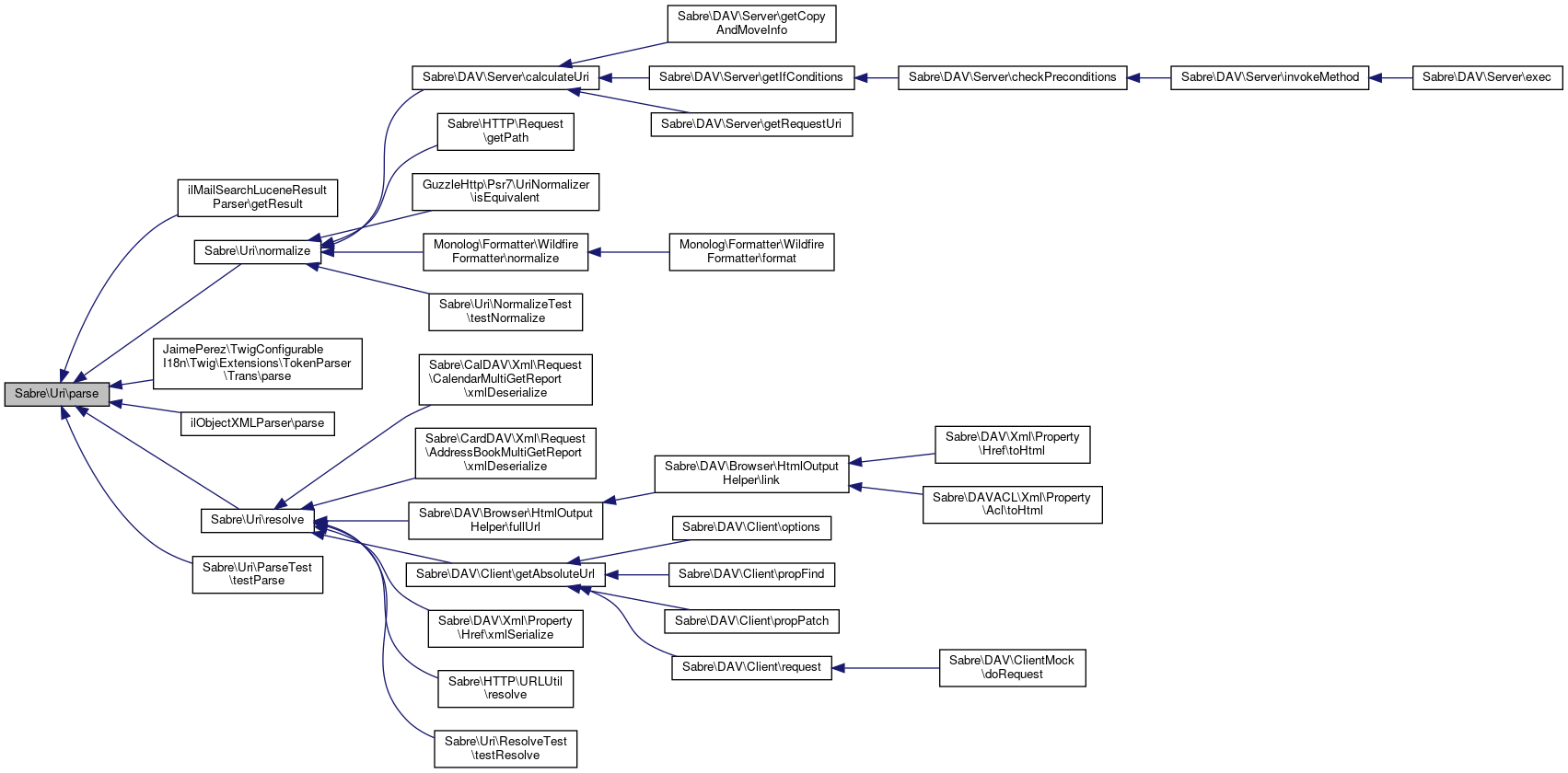
Referenced by Sabre\DAV\Server\calculateUri(), Sabre\HTTP\Request\getPath(), GuzzleHttp\Psr7\UriNormalizer\isEquivalent(), Monolog\Formatter\WildfireFormatter\normalize(), and Sabre\Uri\NormalizeTest\testNormalize().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ parse()
| Sabre\Uri\parse | ( | $uri | ) |
Parses a URI and returns its individual components.
This method largely behaves the same as PHP's parse_url, except that it will return an array with all the array keys, including the ones that are not set by parse_url, which makes it a bit easier to work with.
Unlike PHP's parse_url, it will also convert any non-ascii characters to percent-encoded strings. PHP's parse_url corrupts these characters on OS X.
- Parameters
-
string $uri
- Returns
- array
Definition at line 181 of file functions.php.
References $result, and Sabre\Uri\_parse_fallback().
Referenced by Sabre\Uri\normalize(), ilObjectXMLParser\parse(), JaimePerez\TwigConfigurableI18n\Twig\Extensions\TokenParser\Trans\parse(), Sabre\VObject\ITip\Broker\parseEventForAttendee(), Sabre\Uri\resolve(), Symfony\Component\Yaml\Tests\ParserTest\testCommentAtTheRootIndent(), Symfony\Component\Yaml\Tests\ParserTest\testEmptyValue(), Symfony\Component\Yaml\Tests\ParserTest\testFoldedStringBlockWithComments(), Symfony\Component\Yaml\Tests\ParserTest\testMappingDuplicateKeyBlock(), Symfony\Component\Yaml\Tests\ParserTest\testMappingDuplicateKeyFlow(), Symfony\Component\Yaml\Tests\ParserTest\testMappingInASequence(), Symfony\Component\Yaml\Tests\ParserTest\testMultipleDocumentsNotSupportedException(), Symfony\Component\Yaml\Tests\ParserTest\testNestedFoldedStringBlockWithComments(), Sabre\Uri\ParseTest\testParse(), Symfony\Component\Yaml\Tests\ParserTest\testReferenceResolvingInInlineStrings(), Symfony\Component\Yaml\Tests\ParserTest\testScalarInSequence(), Symfony\Component\Yaml\Tests\ParserTest\testSequenceInAMapping(), and Symfony\Component\Yaml\Tests\ParserTest\testStringBlockWithComments().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ resolve()
| Sabre\Uri\resolve | ( | $basePath, | |
| $newPath | |||
| ) |
This file contains all the uri handling functions.
- Copyright
- Copyright (C) fruux GmbH (https://fruux.com/)
This function takes a basePath, which itself may also be relative, and then applies the relative path on top of it.
- Parameters
-
string $basePath string $newPath
- Returns
- string
Definition at line 23 of file functions.php.
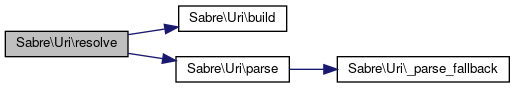
References $base, $path, Sabre\Uri\build(), and Sabre\Uri\parse().
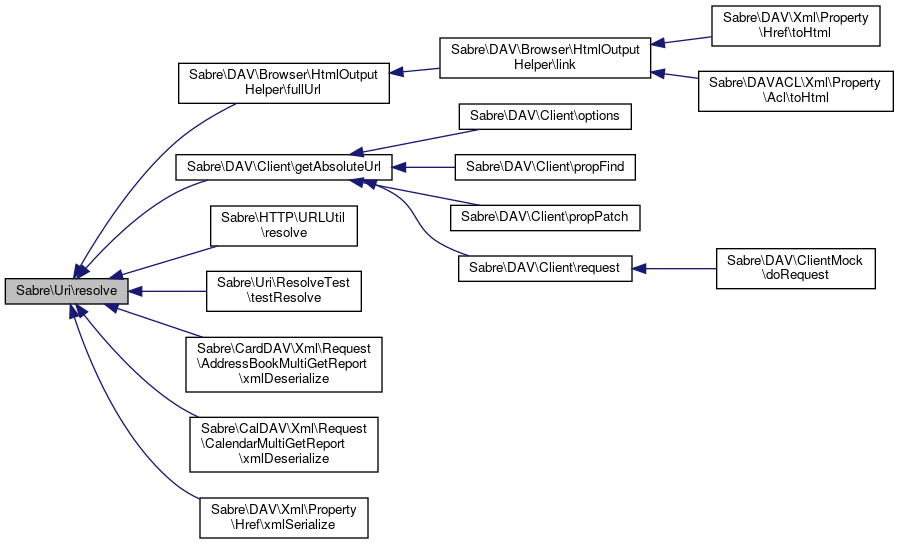
Referenced by Sabre\DAV\Browser\HtmlOutputHelper\fullUrl(), Sabre\DAV\Client\getAbsoluteUrl(), Sabre\HTTP\URLUtil\resolve(), Sabre\Uri\ResolveTest\testResolve(), Sabre\CalDAV\Xml\Request\CalendarMultiGetReport\xmlDeserialize(), Sabre\CardDAV\Xml\Request\AddressBookMultiGetReport\xmlDeserialize(), and Sabre\DAV\Xml\Property\Href\xmlSerialize().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ split()
| Sabre\Uri\split | ( | $path | ) |
Returns the 'dirname' and 'basename' for a path.
The reason there is a custom function for this purpose, is because basename() is locale aware (behaviour changes if C locale or a UTF-8 locale is used) and we need a method that just operates on UTF-8 characters.
In addition basename and dirname are platform aware, and will treat backslash () as a directory separator on windows.
This method returns the 2 components as an array.
If there is no dirname, it will return an empty string. Any / appearing at the end of the string is stripped off.
- Parameters
-
string $path
- Returns
- array
Definition at line 279 of file functions.php.
References $path.
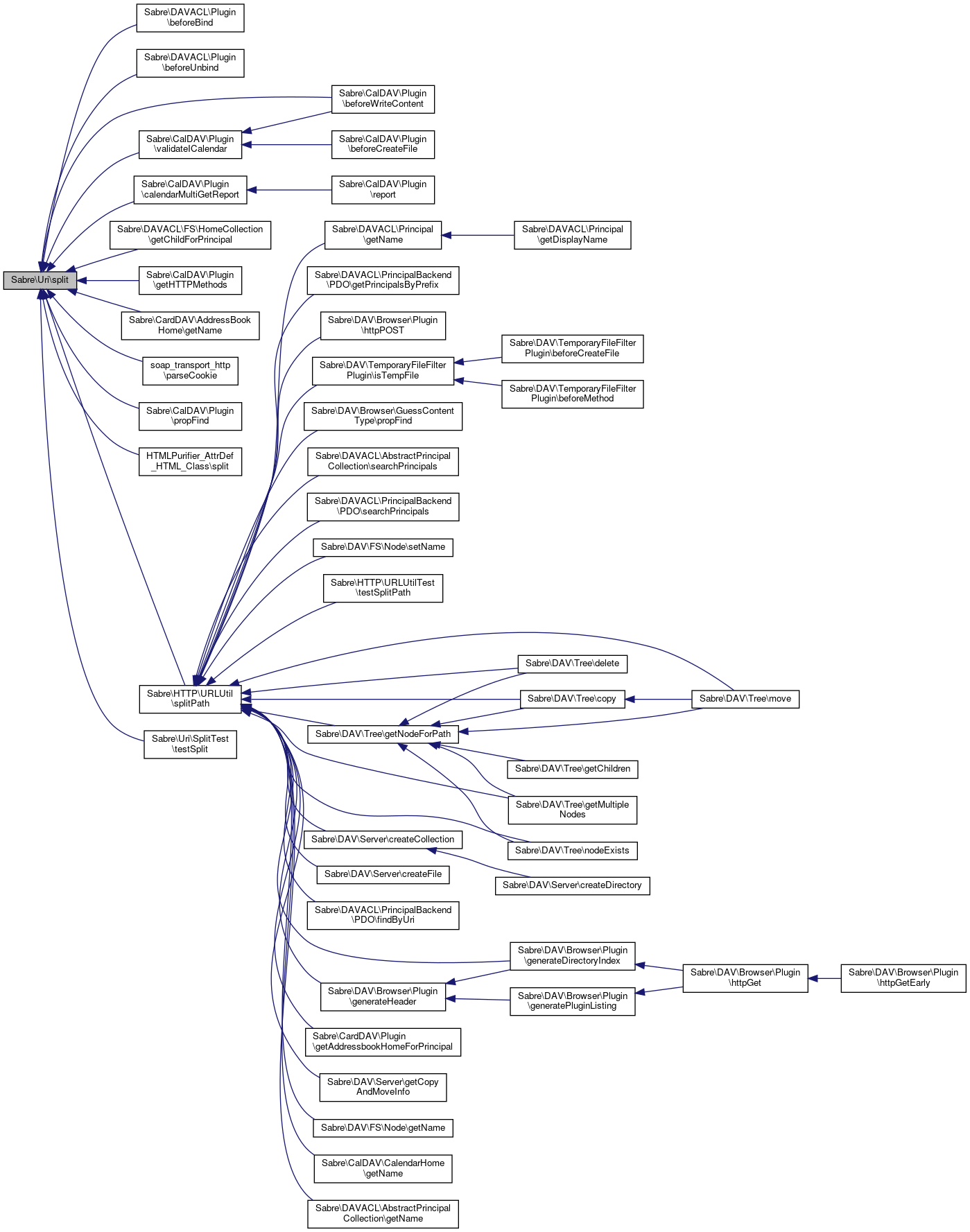
Referenced by Sabre\DAVACL\Plugin\beforeBind(), Sabre\DAVACL\Plugin\beforeUnbind(), Sabre\CalDAV\Plugin\beforeWriteContent(), Sabre\CalDAV\Plugin\calendarMultiGetReport(), Sabre\DAVACL\FS\HomeCollection\getChildForPrincipal(), Sabre\CalDAV\Plugin\getHTTPMethods(), Sabre\CardDAV\AddressBookHome\getName(), soap_transport_http\parseCookie(), Sabre\CalDAV\Plugin\propFind(), HTMLPurifier_AttrDef_HTML_Class\split(), Sabre\HTTP\URLUtil\splitPath(), Sabre\Uri\SplitTest\testSplit(), and Sabre\CalDAV\Plugin\validateICalendar().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function: