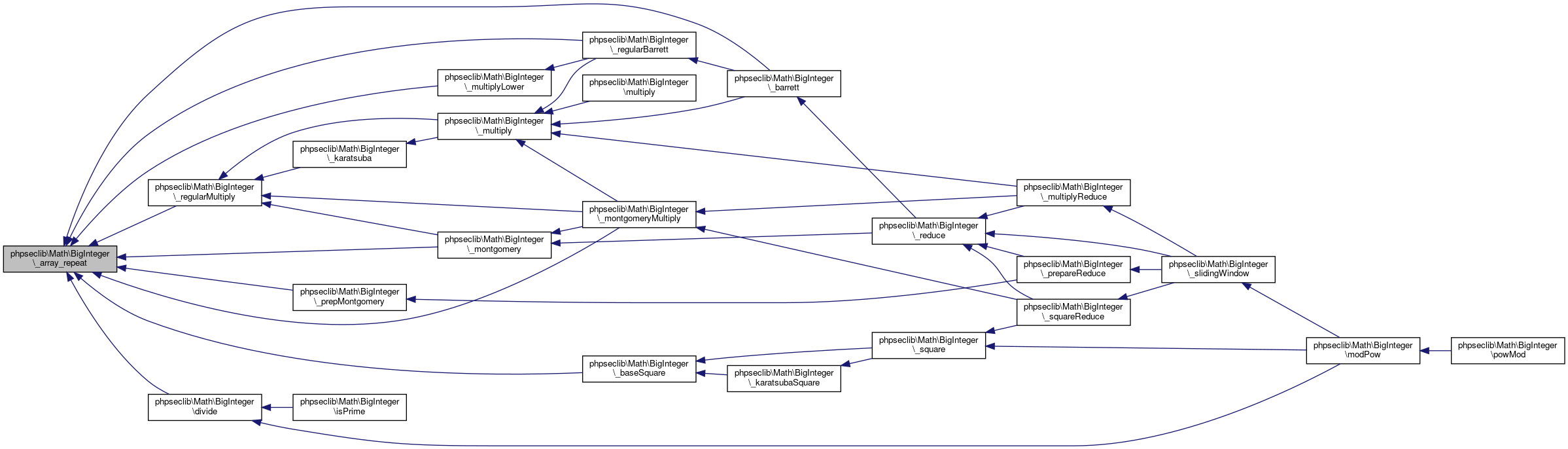
Collaboration diagram for phpseclib\Math\BigInteger:
Collaboration diagram for phpseclib\Math\BigInteger:Public Member Functions | |
| __construct ($x=0, $base=10) | |
| Converts base-2, base-10, base-16, and binary strings (base-256) to BigIntegers. More... | |
| toBytes ($twos_compliment=false) | |
| Converts a BigInteger to a byte string (eg. More... | |
| toHex ($twos_compliment=false) | |
| Converts a BigInteger to a hex string (eg. More... | |
| toBits ($twos_compliment=false) | |
| Converts a BigInteger to a bit string (eg. More... | |
| toString () | |
| Converts a BigInteger to a base-10 number. More... | |
| copy () | |
| Copy an object. More... | |
| __toString () | |
| __toString() magic method More... | |
| __clone () | |
| __clone() magic method More... | |
| __sleep () | |
| __sleep() magic method More... | |
| __wakeup () | |
| __wakeup() magic method More... | |
| __debugInfo () | |
| __debugInfo() magic method More... | |
| add ($y) | |
| Adds two BigIntegers. More... | |
| _add ($x_value, $x_negative, $y_value, $y_negative) | |
| Performs addition. More... | |
| subtract ($y) | |
| Subtracts two BigIntegers. More... | |
| _subtract ($x_value, $x_negative, $y_value, $y_negative) | |
| Performs subtraction. More... | |
| multiply ($x) | |
| Multiplies two BigIntegers. More... | |
| _multiply ($x_value, $x_negative, $y_value, $y_negative) | |
| Performs multiplication. More... | |
| _regularMultiply ($x_value, $y_value) | |
| Performs long multiplication on two BigIntegers. More... | |
| _karatsuba ($x_value, $y_value) | |
| Performs Karatsuba multiplication on two BigIntegers. More... | |
| _square ($x=false) | |
| Performs squaring. More... | |
| _baseSquare ($value) | |
| Performs traditional squaring on two BigIntegers. More... | |
| _karatsubaSquare ($value) | |
| Performs Karatsuba "squaring" on two BigIntegers. More... | |
| divide ($y) | |
| Divides two BigIntegers. More... | |
| _divide_digit ($dividend, $divisor) | |
| Divides a BigInteger by a regular integer. More... | |
| modPow ($e, $n) | |
| Performs modular exponentiation. More... | |
| powMod ($e, $n) | |
| Performs modular exponentiation. More... | |
| _slidingWindow ($e, $n, $mode) | |
| Sliding Window k-ary Modular Exponentiation. More... | |
| _reduce ($x, $n, $mode) | |
| Modular reduction. More... | |
| _prepareReduce ($x, $n, $mode) | |
| Modular reduction preperation. More... | |
| _multiplyReduce ($x, $y, $n, $mode) | |
| Modular multiply. More... | |
| _squareReduce ($x, $n, $mode) | |
| Modular square. More... | |
| _mod2 ($n) | |
| Modulos for Powers of Two. More... | |
| _barrett ($n, $m) | |
| Barrett Modular Reduction. More... | |
| _regularBarrett ($x, $n) | |
| (Regular) Barrett Modular Reduction More... | |
| _multiplyLower ($x_value, $x_negative, $y_value, $y_negative, $stop) | |
| Performs long multiplication up to $stop digits. More... | |
| _montgomery ($x, $n) | |
| Montgomery Modular Reduction. More... | |
| _montgomeryMultiply ($x, $y, $m) | |
| Montgomery Multiply. More... | |
| _prepMontgomery ($x, $n) | |
| Prepare a number for use in Montgomery Modular Reductions. More... | |
| _modInverse67108864 ($x) | |
| Modular Inverse of a number mod 2**26 (eg. More... | |
| modInverse ($n) | |
| Calculates modular inverses. More... | |
| extendedGCD ($n) | |
| Calculates the greatest common divisor and Bezout's identity. More... | |
| gcd ($n) | |
| Calculates the greatest common divisor. More... | |
| abs () | |
| Absolute value. More... | |
| compare ($y) | |
| Compares two numbers. More... | |
| _compare ($x_value, $x_negative, $y_value, $y_negative) | |
| Compares two numbers. More... | |
| equals ($x) | |
| Tests the equality of two numbers. More... | |
| setPrecision ($bits) | |
| Set Precision. More... | |
| bitwise_and ($x) | |
| Logical And. More... | |
| bitwise_or ($x) | |
| Logical Or. More... | |
| bitwise_xor ($x) | |
| Logical Exclusive-Or. More... | |
| bitwise_not () | |
| Logical Not. More... | |
| bitwise_rightShift ($shift) | |
| Logical Right Shift. More... | |
| bitwise_leftShift ($shift) | |
| Logical Left Shift. More... | |
| bitwise_leftRotate ($shift) | |
| Logical Left Rotate. More... | |
| bitwise_rightRotate ($shift) | |
| Logical Right Rotate. More... | |
| _random_number_helper ($size) | |
| Generates a random BigInteger. More... | |
| random ($arg1, $arg2=false) | |
| Generate a random number. More... | |
| randomPrime ($arg1, $arg2=false, $timeout=false) | |
| Generate a random prime number. More... | |
| _make_odd () | |
| Make the current number odd. More... | |
| isPrime ($t=false) | |
| Checks a numer to see if it's prime. More... | |
| _lshift ($shift) | |
| Logical Left Shift. More... | |
| _rshift ($shift) | |
| Logical Right Shift. More... | |
| _normalize ($result) | |
| Normalize. More... | |
| _trim ($value) | |
| Trim. More... | |
| _array_repeat ($input, $multiplier) | |
| Array Repeat. More... | |
| _base256_lshift (&$x, $shift) | |
| Logical Left Shift. More... | |
| _base256_rshift (&$x, $shift) | |
| Logical Right Shift. More... | |
| _int2bytes ($x) | |
| Converts 32-bit integers to bytes. More... | |
| _bytes2int ($x) | |
| Converts bytes to 32-bit integers. More... | |
| _encodeASN1Length ($length) | |
| DER-encode an integer. More... | |
| _safe_divide ($x, $y) | |
| Single digit division. More... | |
Data Fields | |
| const | MONTGOMERY = 0 |
| #+ Reduction constants More... | |
| const | BARRETT = 1 |
| const | POWEROF2 = 2 |
| const | CLASSIC = 3 |
| const | NONE = 4 |
| const | VALUE = 0 |
| #- More... | |
| const | SIGN = 1 |
| $result[self::SIGN] contains the sign. More... | |
| const | VARIABLE = 0 |
| #- More... | |
| const | DATA = 1 |
| $cache[self::DATA] contains the cached data. More... | |
| const | MODE_INTERNAL = 1 |
| #- More... | |
| const | MODE_BCMATH = 2 |
| To use the BCMath library. More... | |
| const | MODE_GMP = 3 |
| To use the GMP library. More... | |
| const | KARATSUBA_CUTOFF = 25 |
| #- More... | |
| $value | |
| $is_negative = false | |
| $precision = -1 | |
| Precision. More... | |
| $bitmask = false | |
| Precision Bitmask. More... | |
| $hex | |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| static | $base |
| #+ Static properties used by the pure-PHP implementation. More... | |
| static | $baseFull |
| static | $maxDigit |
| static | $msb |
| static | $max10 |
| $max10 in greatest $max10Len satisfying $max10 = 10**$max10Len <= 2**$base. More... | |
| static | $max10Len |
| $max10Len in greatest $max10Len satisfying $max10 = 10**$max10Len <= 2**$base. More... | |
| static | $maxDigit2 |
Detailed Description
Definition at line 63 of file BigInteger.php.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ __construct()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::__construct | ( | $x = 0, |
|
$base = 10 |
|||
| ) |
Converts base-2, base-10, base-16, and binary strings (base-256) to BigIntegers.
If the second parameter - $base - is negative, then it will be assumed that the number's are encoded using two's compliment. The sole exception to this is -10, which is treated the same as 10 is.
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('0x32', 16); // 50 in base-16
echo $a->toString(); // outputs 50 ?>
- Parameters
-
$x base-10 number or base-$base number if $base set. int $base
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 252 of file BigInteger.php.
References $base, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$base, $i, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$is_negative, $m, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value, $x, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_base256_rshift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_bytes2int(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_int2bytes(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\abs(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:Member Function Documentation
◆ __clone()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::__clone | ( | ) |
__clone() magic method
Although you can call BigInteger::__toString() directly in PHP5, you cannot call BigInteger::__clone() directly in PHP5. You can in PHP4 since it's not a magic method, but in PHP5, you have to call it by using the PHP5 only syntax of $y = clone $x. As such, if you're trying to write an application that works on both PHP4 and PHP5, call BigInteger::copy(), instead.
@access public
- See also
- self::copy()
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger
Definition at line 764 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ __debugInfo()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::__debugInfo | ( | ) |
__debugInfo() magic method
Will be called, automatically, when print_r() or var_dump() are called
@access public
Definition at line 813 of file BigInteger.php.
References $engine, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_INTERNAL, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toHex().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ __sleep()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::__sleep | ( | ) |
__sleep() magic method
Will be called, automatically, when serialize() is called on a BigInteger object.
- See also
- self::__wakeup() @access User interface
Definition at line 777 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toHex().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ __toString()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::__toString | ( | ) |
__toString() magic method
Will be called, automatically, if you're supporting just PHP5. If you're supporting PHP4, you'll need to call toString().
@access public
Definition at line 747 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toString().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ __wakeup()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::__wakeup | ( | ) |
__wakeup() magic method
Will be called, automatically, when unserialize() is called on a BigInteger object.
- See also
- self::__sleep() @access User interface
Definition at line 795 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$hex, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\setPrecision().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ _add()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_add | ( | $x_value, | |
| $x_negative, | |||
| $y_value, | |||
| $y_negative | |||
| ) |
Performs addition.
- Parameters
-
array $x_value bool $x_negative array $y_value bool $y_negative
- Returns
- array @access private
Definition at line 893 of file BigInteger.php.
References $base, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$baseFull, $i, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$maxDigit, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$maxDigit2, $size, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_compare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_trim(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\SIGN.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_barrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsuba(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsubaSquare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomery(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularBarrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\add().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _array_repeat()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_array_repeat | ( | $input, | |
| $multiplier | |||
| ) |
Array Repeat.
- Parameters
-
$input Array $multiplier mixed
- Returns
- array @access private
Definition at line 3609 of file BigInteger.php.
References $input.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_barrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_baseSquare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomery(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiplyLower(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_prepMontgomery(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularBarrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularMultiply(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\divide().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
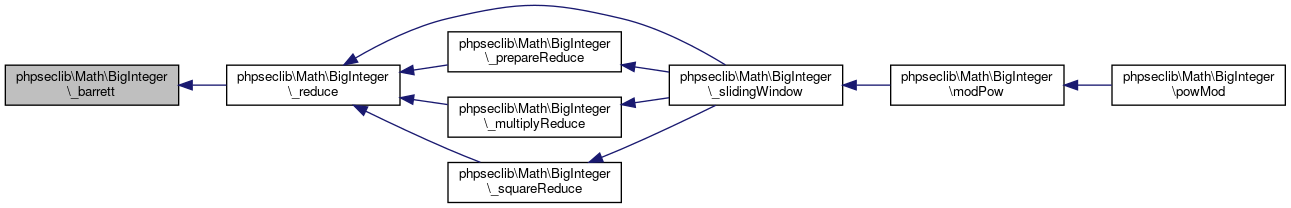
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _barrett()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_barrett | ( | $n, | |
| $m | |||
| ) |
Barrett Modular Reduction.
See HAC 14.3.3 / MPM 6.2.5 for more information. Modified slightly, so as not to require negative numbers (initially, this script didn't support negative numbers).
Employs "folding", as described at thesis-149.pdf#page=66. To quote from it, "the idea [behind folding] is to find a value x' such that x (mod m) = x' (mod m), with x' being smaller than x."
Unfortunately, the "Barrett Reduction with Folding" algorithm described in thesis-149.pdf is not, as written, all that usable on account of (1) its not using reasonable radix points as discussed in MPM 6.2.2 and (2) the fact that, even with reasonable radix points, it only works when there are an even number of digits in the denominator. The reason for (2) is that (x >> 1) + (x >> 1) != x / 2 + x / 2. If x is even, they're the same, but if x is odd, they're not. See the in-line comments for details.
- See also
- self::_slidingWindow() @access private
- Parameters
-
array $n array $m
- Returns
- array
Definition at line 2013 of file BigInteger.php.
References $key, $m, $n, $result, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_array_repeat(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_compare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularBarrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_trim(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\DATA, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VALUE, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VARIABLE.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_reduce().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _base256_lshift()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_base256_lshift | ( | & | $x, |
| $shift | |||
| ) |
Logical Left Shift.
Shifts binary strings $shift bits, essentially multiplying by 2**$shift.
- Parameters
-
$x String $shift Integer
- Returns
- string @access private
Definition at line 3624 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_not().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _base256_rshift()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_base256_rshift | ( | & | $x, |
| $shift | |||
| ) |
Logical Right Shift.
Shifts binary strings $shift bits, essentially dividing by 2**$shift and returning the remainder.
- Parameters
-
$x String $shift Integer
- Returns
- string @access private
Definition at line 3653 of file BigInteger.php.
References $i, $start, and $x.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__construct().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _baseSquare()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_baseSquare | ( | $value | ) |
Performs traditional squaring on two BigIntegers.
Squaring can be done faster than multiplying a number by itself can be. See HAC 14.2.4 / MPM 5.3 for more information.
- Parameters
-
array $value
- Returns
- array @access private
Definition at line 1312 of file BigInteger.php.
References $base, $i, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_array_repeat().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsubaSquare(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_square().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _bytes2int()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_bytes2int | ( | $x | ) |
Converts bytes to 32-bit integers.
- Parameters
-
string $x
- Returns
- int @access private
Definition at line 3706 of file BigInteger.php.
References $x.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__construct().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _compare()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_compare | ( | $x_value, | |
| $x_negative, | |||
| $y_value, | |||
| $y_negative | |||
| ) |
Compares two numbers.
- Parameters
-
array $x_value bool $x_negative array $y_value bool $y_negative
- Returns
- int
- See also
- self::compare() @access private
Definition at line 2701 of file BigInteger.php.
References $i, $result, and $size.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_barrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomery(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularBarrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\compare().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _divide_digit()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_divide_digit | ( | $dividend, | |
| $divisor | |||
| ) |
Divides a BigInteger by a regular integer.
abc / x = a00 / x + b0 / x + c / x
- Parameters
-
array $dividend array $divisor
- Returns
- array @access private
Definition at line 1587 of file BigInteger.php.
References $i, $result, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_safe_divide().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\divide(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\isPrime().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _encodeASN1Length()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_encodeASN1Length | ( | $length | ) |
DER-encode an integer.
The ability to DER-encode integers is needed to create RSA public keys for use with OpenSSL
- See also
- self::modPow() @access private
- Parameters
-
int $length
- Returns
- string
Definition at line 3722 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modPow().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _int2bytes()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_int2bytes | ( | $x | ) |
Converts 32-bit integers to bytes.
- Parameters
-
int $x
- Returns
- string @access private
Definition at line 3694 of file BigInteger.php.
References $x.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__construct(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _karatsuba()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_karatsuba | ( | $x_value, | |
| $y_value | |||
| ) |
Performs Karatsuba multiplication on two BigIntegers.
See Karatsuba algorithm and MPM 5.2.3.
- Parameters
-
array $x_value array $y_value
- Returns
- array @access private
Definition at line 1256 of file BigInteger.php.
References $m, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsuba(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularMultiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VALUE.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsuba(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiply().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _karatsubaSquare()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_karatsubaSquare | ( | $value | ) |
Performs Karatsuba "squaring" on two BigIntegers.
See Karatsuba algorithm and MPM 5.3.4.
- Parameters
-
array $value
- Returns
- array @access private
Definition at line 1351 of file BigInteger.php.
References $m, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_baseSquare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsubaSquare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VALUE.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsubaSquare(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_square().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _lshift()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_lshift | ( | $shift | ) |
Logical Left Shift.
Shifts BigInteger's by $shift bits.
- Parameters
-
int $shift @access private
Definition at line 3469 of file BigInteger.php.
References $base, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$base, and $i.
◆ _make_odd()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_make_odd | ( | ) |
Make the current number odd.
If the current number is odd it'll be unchanged. If it's even, one will be added to it.
- See also
- self::randomPrime() @access private
Definition at line 3290 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
◆ _mod2()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_mod2 | ( | $n | ) |
Modulos for Powers of Two.
Calculates $x$n, where $n = 2**$e, for some $e. Since this is basically the same as doing $x & ($n-1), we'll just use this function as a wrapper for doing that.
- See also
- self::_slidingWindow() @access private
- Parameters
-
phpseclib\Math\BigInteger
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger
Definition at line 1982 of file BigInteger.php.
References $n, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_and().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ _modInverse67108864()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_modInverse67108864 | ( | $x | ) |
Modular Inverse of a number mod 2**26 (eg.
67108864)
Based off of the bnpInvDigit function implemented and justified in the following URL:
http://www-cs-students.stanford.edu/~tjw/jsbn/jsbn.js
The following URL provides more info:
http://groups.google.com/group/sci.crypt/msg/7a137205c1be7d85
As for why we do all the bitmasking... strange things can happen when converting from floats to ints. For instance, on some computers, var_dump((int) -4294967297) yields int(-1) and on others, it yields int(-2147483648). To avoid problems stemming from this, we use bitmasks to guarantee that ints aren't auto-converted to floats. The outermost bitmask is present because without it, there's no guarantee that the "residue" returned would be the so-called "common residue". We use fmod, in the last step, because the maximum possible $x is 26 bits and the maximum $result is 16 bits. Thus, we have to be able to handle up to 40 bits, which only 64-bit floating points will support.
Thanks to Pedro Gimeno Fortea for input!
- See also
- self::_montgomery() @access private
- Parameters
-
array $x
- Returns
- int
Definition at line 2399 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$maxDigit, $result, and $x.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomery(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _montgomery()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_montgomery | ( | $x, | |
| $n | |||
| ) |
Montgomery Modular Reduction.
($x->_prepMontgomery($n))->_montgomery($n) yields $x % $n. MPM 6.3 provides insights on how this can be improved upon (basically, by using the comba method). gcd($n, 2) must be equal to one for this function to work correctly.
- See also
- self::_prepMontgomery()
- self::_slidingWindow() @access private
- Parameters
-
array $x array $n
- Returns
- array
Definition at line 2263 of file BigInteger.php.
References $base, $i, $key, $n, $result, $x, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_array_repeat(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_compare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_modInverse67108864(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularMultiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\DATA, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VALUE, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VARIABLE.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_reduce().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _montgomeryMultiply()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_montgomeryMultiply | ( | $x, | |
| $y, | |||
| $m | |||
| ) |
Montgomery Multiply.
Interleaves the montgomery reduction and long multiplication algorithms together as described in HAC 14.36
- See also
- self::_prepMontgomery()
- self::_montgomery() @access private
- Parameters
-
array $x array $y array $m
- Returns
- array
Definition at line 2311 of file BigInteger.php.
References $base, $i, $key, $m, $n, $x, $y, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_array_repeat(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_compare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_modInverse67108864(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomery(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularMultiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\DATA, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VALUE, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VARIABLE.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiplyReduce(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_squareReduce().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _multiply()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_multiply | ( | $x_value, | |
| $x_negative, | |||
| $y_value, | |||
| $y_negative | |||
| ) |
Performs multiplication.
- Parameters
-
array $x_value bool $x_negative array $y_value bool $y_negative
- Returns
- array @access private
Definition at line 1155 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsuba(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularMultiply(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_trim().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_barrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiplyReduce(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularBarrett(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\multiply().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _multiplyLower()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_multiplyLower | ( | $x_value, | |
| $x_negative, | |||
| $y_value, | |||
| $y_negative, | |||
| $stop | |||
| ) |
Performs long multiplication up to $stop digits.
If you're going to be doing array_slice($product->value, 0, $stop), some cycles can be saved.
- See also
- self::_regularBarrett()
- Parameters
-
array $x_value bool $x_negative array $y_value bool $y_negative int $stop
- Returns
- array @access private
Definition at line 2184 of file BigInteger.php.
References $base, $i, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_array_repeat(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_trim().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularBarrett().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _multiplyReduce()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_multiplyReduce | ( | $x, | |
| $y, | |||
| $n, | |||
| $mode | |||
| ) |
Modular multiply.
- See also
- self::_slidingWindow() @access private
- Parameters
-
array $x array $y array $n int $mode
- Returns
- array
Definition at line 1944 of file BigInteger.php.
References $n, $x, $y, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiply(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_reduce().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_slidingWindow().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _normalize()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_normalize | ( | $result | ) |
Normalize.
Removes leading zeros and truncates (if necessary) to maintain the appropriate precision
- Parameters
-
phpseclib\Math\BigInteger
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger
- See also
- self::_trim() @access private
Definition at line 3540 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$bitmask, $i, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$precision, $result, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_trim(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_and(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_leftRotate(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_leftShift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_not(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_or(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_rightShift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_xor(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\divide(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\extendedGCD(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modInverse(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modPow(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\multiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\random(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\setPrecision(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\subtract().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _prepareReduce()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_prepareReduce | ( | $x, | |
| $n, | |||
| $mode | |||
| ) |
Modular reduction preperation.
- See also
- self::_slidingWindow() @access private
- Parameters
-
array $x array $n int $mode
- Returns
- array
Definition at line 1925 of file BigInteger.php.
References $n, $x, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_prepMontgomery(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_reduce().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_slidingWindow().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _prepMontgomery()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_prepMontgomery | ( | $x, | |
| $n | |||
| ) |
Prepare a number for use in Montgomery Modular Reductions.
- See also
- self::_montgomery()
- self::_slidingWindow() @access private
- Parameters
-
array $x array $n
- Returns
- array
Definition at line 2362 of file BigInteger.php.
References $n, $x, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_array_repeat().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_prepareReduce().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _random_number_helper()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_random_number_helper | ( | $size | ) |
Generates a random BigInteger.
Byte length is equal to $length. Uses \phpseclib\Crypt\Random if it's loaded and mt_rand if it's not.
- Parameters
-
int $length
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access private
Definition at line 3072 of file BigInteger.php.
References $i, $size, and phpseclib\Crypt\Random\string().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\random().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _reduce()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_reduce | ( | $x, | |
| $n, | |||
| $mode | |||
| ) |
Modular reduction.
For most $modes this will return the remainder.
- See also
- self::_slidingWindow() @access private
- Parameters
-
array $x array $n int $mode
- Returns
- array
Definition at line 1888 of file BigInteger.php.
References $n, $x, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_barrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomery(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\BARRETT, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\CLASSIC, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MONTGOMERY, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\NONE, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\POWEROF2.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiplyReduce(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_prepareReduce(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_slidingWindow(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_squareReduce().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _regularBarrett()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_regularBarrett | ( | $x, | |
| $n | |||
| ) |
(Regular) Barrett Modular Reduction
For numbers with more than four digits BigInteger::_barrett() is faster. The difference between that and this is that this function does not fold the denominator into a smaller form.
- See also
- self::_slidingWindow() @access private
- Parameters
-
array $x array $n
- Returns
- array
Definition at line 2110 of file BigInteger.php.
References $key, $n, $result, $x, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_array_repeat(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_compare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiplyLower(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\DATA, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VALUE, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VARIABLE.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_barrett().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _regularMultiply()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_regularMultiply | ( | $x_value, | |
| $y_value | |||
| ) |
Performs long multiplication on two BigIntegers.
Modeled after 'multiply' in MutableBigInteger.java.
- Parameters
-
array $x_value array $y_value
- Returns
- array @access private
Definition at line 1192 of file BigInteger.php.
References $base, $i, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_array_repeat().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsuba(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomery(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiply().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _rshift()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_rshift | ( | $shift | ) |
Logical Right Shift.
Shifts BigInteger's by $shift bits.
- Parameters
-
int $shift @access private
Definition at line 3504 of file BigInteger.php.
References $base, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$base, $i, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_trim().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ _safe_divide()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_safe_divide | ( | $x, | |
| $y | |||
| ) |
Single digit division.
Even if int64 is being used the division operator will return a float64 value if the dividend is not evenly divisible by the divisor. Since a float64 doesn't have the precision of int64 this is a problem so, when int64 is being used, we'll guarantee that the dividend is divisible by first subtracting the remainder.
@access private
- Parameters
-
int $x int $y
- Returns
- int
Definition at line 3745 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_divide_digit(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\divide().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _slidingWindow()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_slidingWindow | ( | $e, | |
| $n, | |||
| $mode | |||
| ) |
Sliding Window k-ary Modular Exponentiation.
Based on HAC 14.85 / MPM 7.7. In a departure from those algorithims, however, this function performs a modular reduction after every multiplication and squaring operation. As such, this function has the same preconditions that the reductions being used do.
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $e \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $n int $mode
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access private
Definition at line 1811 of file BigInteger.php.
References $base, $i, $n, $result, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiplyReduce(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_prepareReduce(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_reduce(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_squareReduce().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modPow().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _square()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_square | ( | $x = false | ) |
Performs squaring.
- Parameters
-
array $x
- Returns
- array @access private
Definition at line 1294 of file BigInteger.php.
References $x, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_baseSquare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsubaSquare(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_trim().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_squareReduce(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modPow().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _squareReduce()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_squareReduce | ( | $x, | |
| $n, | |||
| $mode | |||
| ) |
Modular square.
- See also
- self::_slidingWindow() @access private
- Parameters
-
array $x array $n int $mode
- Returns
- array
Definition at line 1963 of file BigInteger.php.
References $n, $x, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_reduce(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_square().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_slidingWindow().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _subtract()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_subtract | ( | $x_value, | |
| $x_negative, | |||
| $y_value, | |||
| $y_negative | |||
| ) |
Performs subtraction.
- Parameters
-
array $x_value bool $x_negative array $y_value bool $y_negative
- Returns
- array @access private
Definition at line 1022 of file BigInteger.php.
References $base, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$baseFull, $i, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$maxDigit, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$maxDigit2, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_compare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_trim(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\SIGN.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_barrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsuba(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsubaSquare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomery(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularBarrett(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\subtract().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ _trim()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::_trim | ( | $value | ) |
Trim.
Removes leading zeros
- Parameters
-
array $value
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access private
Definition at line 3589 of file BigInteger.php.
References $i, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_barrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiplyLower(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_rshift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_square(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ abs()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::abs | ( | ) |
Absolute value.
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 2642 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__construct(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modInverse().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ add()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::add | ( | $y | ) |
Adds two BigIntegers.
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('10'); $b = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('20');
$c = $a->add($b);
echo $c->toString(); // outputs 30 ?>
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $y
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 859 of file BigInteger.php.
References $result, $y, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\SIGN, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VALUE.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__construct(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ bitwise_and()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::bitwise_and | ( | $x | ) |
Logical And.
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $x @access public
Definition at line 2776 of file BigInteger.php.
References $i, $result, $x, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_mod2().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ bitwise_leftRotate()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::bitwise_leftRotate | ( | $shift | ) |
Logical Left Rotate.
Instead of the top x bits being dropped they're appended to the shifted bit string.
- Parameters
-
int $shift
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 3013 of file BigInteger.php.
References $i, $mask, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$precision, $result, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_leftShift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_rightShift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_rightRotate().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ bitwise_leftShift()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::bitwise_leftShift | ( | $shift | ) |
Logical Left Shift.
Shifts BigInteger's by $shift bits, effectively multiplying by 2**$shift.
- Parameters
-
int $shift
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 2976 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_leftRotate().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ bitwise_not()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::bitwise_not | ( | ) |
Logical Not.
@access public
Definition at line 2896 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$msb, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_base256_lshift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ bitwise_or()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::bitwise_or | ( | $x | ) |
Logical Or.
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $x @access public
Definition at line 2817 of file BigInteger.php.
References $i, $result, $x, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ bitwise_rightRotate()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::bitwise_rightRotate | ( | $shift | ) |
Logical Right Rotate.
Instead of the bottom x bits being dropped they're prepended to the shifted bit string.
- Parameters
-
int $shift
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 3058 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_leftRotate().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ bitwise_rightShift()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::bitwise_rightShift | ( | $shift | ) |
Logical Right Shift.
Shifts BigInteger's by $shift bits, effectively dividing by 2**$shift.
- Parameters
-
int $shift
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 2938 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_leftRotate().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ bitwise_xor()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::bitwise_xor | ( | $x | ) |
Logical Exclusive-Or.
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $x @access public
Definition at line 2857 of file BigInteger.php.
References $i, $result, $x, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ compare()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::compare | ( | $y | ) |
Compares two numbers.
Although one might think !$x->compare($y) means $x != $y, it, in fact, means the opposite. The reason for this is demonstrated thusly:
$x > $y: $x->compare($y) > 0 $x < $y: $x->compare($y) < 0 $x == $y: $x->compare($y) == 0
Note how the same comparison operator is used. If you want to test for equality, use $x->equals($y).
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $y
- Returns
- int < 0 if $this is less than $y; > 0 if $this is greater than $y, and 0 if they are equal. @access public
- See also
- self::equals()
Definition at line 2678 of file BigInteger.php.
References $y, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_compare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modInverse(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modPow(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBits(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ copy()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::copy | ( | ) |
Copy an object.
PHP5 passes objects by reference while PHP4 passes by value. As such, we need a function to guarantee that all objects are passed by value, when appropriate. More information can be found here:
http://php.net/language.oop5.basic#51624
@access public
- See also
- self::__clone()
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger
Definition at line 728 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$bitmask, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$is_negative, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$precision, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__clone(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_and(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_leftRotate(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_or(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_xor(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\divide(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\extendedGCD(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\isPrime(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toString().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ divide()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::divide | ( | $y | ) |
Divides two BigIntegers.
Returns an array whose first element contains the quotient and whose second element contains the "common residue". If the remainder would be positive, the "common residue" and the remainder are the same. If the remainder would be negative, the "common residue" is equal to the sum of the remainder and the divisor (basically, the "common residue" is the first positive modulo).
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('10'); $b = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('20');
list($quotient, $remainder) = $a->divide($b);
echo $quotient->toString(); // outputs 0 echo "\r\n"; echo $remainder->toString(); // outputs 10 ?>
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $y
- Returns
- array @access public
Definition at line 1406 of file BigInteger.php.
References $i, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$maxDigit, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$msb, $r, $x, $y, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_array_repeat(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_divide_digit(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_safe_divide(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\isPrime(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modPow().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ equals()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::equals | ( | $x | ) |
Tests the equality of two numbers.
If you need to see if one number is greater than or less than another number, use BigInteger::compare()
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $x
- Returns
- bool @access public
- See also
- self::compare()
Definition at line 2736 of file BigInteger.php.
References $x, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\isPrime().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ extendedGCD()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::extendedGCD | ( | $n | ) |
Calculates the greatest common divisor and Bezout's identity.
Say you have 693 and 609. The GCD is 21. Bezout's identity states that there exist integers x and y such that 693*x + 609*y == 21. In point of fact, there are actually an infinite number of x and y combinations and which combination is returned is dependant upon which mode is in use. See Bezout's identity - Wikipedia for more information.
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger(693); $b = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger(609);
extract($a->extendedGCD($b));
echo $gcd->toString() . "\r\n"; // outputs 21 echo $a->toString() * $x->toString() + $b->toString() * $y->toString(); // outputs 21 ?>
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $n
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 2501 of file BigInteger.php.
References $c, $d, $n, $s, $t, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value, $x, $y, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\gcd(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modInverse().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ gcd()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::gcd | ( | $n | ) |
Calculates the greatest common divisor.
Say you have 693 and 609. The GCD is 21.
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger(693); $b = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger(609);
$gcd = a->extendedGCD($b);
echo $gcd->toString() . "\r\n"; // outputs 21 ?>
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $n
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 2630 of file BigInteger.php.
References $n, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\extendedGCD().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ isPrime()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::isPrime | ( | $t = false | ) |
Checks a numer to see if it's prime.
Assuming the $t parameter is not set, this function has an error rate of 2**-80. The main motivation for the $t parameter is distributability. BigInteger::randomPrime() can be distributed across multiple pageloads on a website instead of just one.
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $t
- Returns
- bool @access public
Definition at line 3320 of file BigInteger.php.
References $i, $n, $r, $s, $t, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value, $y, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_divide_digit(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\divide(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\equals(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\random(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ modInverse()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::modInverse | ( | $n | ) |
Calculates modular inverses.
Say you have (30 mod 17 * x mod 17) mod 17 == 1. x can be found using modular inverses.
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger(30); $b = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger(17);
$c = $a->modInverse($b); echo $c->toString(); // outputs 4
echo "\r\n";
$d = $a->multiply($c); list(, $d) = $d->divide($b); echo $d; // outputs 1 (as per the definition of modular inverse) ?>
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $n
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger|false @access public
Definition at line 2437 of file BigInteger.php.
References $n, $x, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\abs(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\compare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\extendedGCD(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modPow().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ modPow()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::modPow | ( | $e, | |
| $n | |||
| ) |
Performs modular exponentiation.
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('10'); $b = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('20'); $c = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('30');
$c = $a->modPow($b, $c);
echo $c->toString(); // outputs 10 ?>
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $e \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $n
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 1641 of file BigInteger.php.
References $i, $n, $result, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_encodeASN1Length(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_slidingWindow(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_square(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\compare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\divide(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modInverse(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\powMod().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ multiply()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::multiply | ( | $x | ) |
Multiplies two BigIntegers.
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('10'); $b = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('20');
$c = $a->multiply($b);
echo $c->toString(); // outputs 200 ?>
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $x
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 1121 of file BigInteger.php.
References $x, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_multiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\SIGN, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VALUE.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ powMod()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::powMod | ( | $e, | |
| $n | |||
| ) |
Performs modular exponentiation.
Alias for modPow().
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $e \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $n
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 1792 of file BigInteger.php.
References $n, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modPow().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ random()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::random | ( | $arg1, | |
$arg2 = false |
|||
| ) |
Generate a random number.
Returns a random number between $min and $max where $min and $max can be defined using one of the two methods:
$min->random($max) $max->random($min)
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $arg1 \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $arg2
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 3109 of file BigInteger.php.
References $size, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_random_number_helper().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\isPrime(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\randomPrime().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ randomPrime()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::randomPrime | ( | $arg1, | |
$arg2 = false, |
|||
$timeout = false |
|||
| ) |
Generate a random prime number.
If there's not a prime within the given range, false will be returned. If more than $timeout seconds have elapsed, give up and return false.
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $arg1 \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $arg2 int $timeout
- Returns
- Math_BigInteger|false @access public
Definition at line 3190 of file BigInteger.php.
References $start, $x, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\random().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ setPrecision()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::setPrecision | ( | $bits | ) |
Set Precision.
Some bitwise operations give different results depending on the precision being used. Examples include left shift, not, and rotates.
- Parameters
-
int $bits @access public
Definition at line 2755 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__wakeup().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ subtract()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::subtract | ( | $y | ) |
Subtracts two BigIntegers.
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('10'); $b = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('20');
$c = $a->subtract($b);
echo $c->toString(); // outputs -10 ?>
- Parameters
-
\phpseclib\Math\BigInteger $y
- Returns
- \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger @access public
Definition at line 988 of file BigInteger.php.
References $result, $y, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\SIGN, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\VALUE.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ toBits()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::toBits | ( | $twos_compliment = false | ) |
Converts a BigInteger to a bit string (eg.
base-2).
Negative numbers are saved as positive numbers, unless $twos_compliment is set to true, at which point, they're saved as two's compliment.
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('65');
echo $a->toBits(); // outputs '1000001' ?>
- Parameters
-
bool $twos_compliment
- Returns
- string @access public
Definition at line 642 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$hex, $i, $result, $start, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\compare(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toHex().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ toBytes()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::toBytes | ( | $twos_compliment = false | ) |
Converts a BigInteger to a byte string (eg.
base-256).
Negative numbers are saved as positive numbers, unless $twos_compliment is set to true, at which point, they're saved as two's compliment.
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('65');
echo $a->toBytes(); // outputs chr(65) ?>
- Parameters
-
bool $twos_compliment
- Returns
- string @access public
Definition at line 522 of file BigInteger.php.
References $base, $current, $i, $result, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\$value, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_int2bytes(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\compare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_and(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_leftRotate(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_not(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_or(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_xor(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\isPrime(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modPow(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toHex().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ toHex()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::toHex | ( | $twos_compliment = false | ) |
Converts a BigInteger to a hex string (eg.
base-16)).
Negative numbers are saved as positive numbers, unless $twos_compliment is set to true, at which point, they're saved as two's compliment.
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('65');
echo $a->toHex(); // outputs '41' ?>
- Parameters
-
bool $twos_compliment
- Returns
- string @access public
Definition at line 617 of file BigInteger.php.
References phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes().
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__debugInfo(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__sleep(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBits().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ toString()
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::toString | ( | ) |
Converts a BigInteger to a base-10 number.
Here's an example: <?php $a = new \phpseclib\Math\BigInteger('50');
echo $a->toString(); // outputs 50 ?>
- Returns
- string @access public
Definition at line 677 of file BigInteger.php.
References $result, phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_BCMATH, and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\MODE_GMP.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__toString().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:Field Documentation
◆ $base
|
staticprotected |
#+ Static properties used by the pure-PHP implementation.
- See also
- __construct()
Definition at line 167 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__construct(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_lshift(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_rshift().
◆ $baseFull
|
staticprotected |
Definition at line 168 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract().
◆ $bitmask
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::$bitmask = false |
Precision Bitmask.
- See also
- self::setPrecision() @access private
Definition at line 216 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy().
◆ $hex
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::$hex |
Definition at line 230 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__wakeup(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBits().
◆ $is_negative
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::$is_negative = false |
Definition at line 200 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__construct(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy().
◆ $max10
|
staticprotected |
$max10 in greatest $max10Len satisfying $max10 = 10**$max10Len <= 2**$base.
Definition at line 176 of file BigInteger.php.
◆ $max10Len
|
staticprotected |
$max10Len in greatest $max10Len satisfying $max10 = 10**$max10Len <= 2**$base.
Definition at line 182 of file BigInteger.php.
◆ $maxDigit
|
staticprotected |
Definition at line 169 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_modInverse67108864(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\divide().
◆ $maxDigit2
|
staticprotected |
Definition at line 183 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract().
◆ $msb
|
staticprotected |
Definition at line 170 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_not(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\divide().
◆ $precision
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::$precision = -1 |
Precision.
- See also
- self::setPrecision() @access private
Definition at line 208 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_leftRotate(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy().
◆ $value
| phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::$value |
Definition at line 192 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__construct(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_baseSquare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsubaSquare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_trim(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\abs(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_leftShift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_rightShift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\copy(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\extendedGCD(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\isPrime(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes().
◆ BARRETT
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::BARRETT = 1 |
- See also
- BigInteger::_barrett()
Definition at line 79 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_reduce().
◆ CLASSIC
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::CLASSIC = 3 |
- See also
- BigInteger::_remainder()
Definition at line 87 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_reduce().
◆ DATA
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::DATA = 1 |
$cache[self::DATA] contains the cached data.
Definition at line 126 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_barrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomery(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularBarrett().
◆ KARATSUBA_CUTOFF
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::KARATSUBA_CUTOFF = 25 |
#-
Karatsuba Cutoff
At what point do we switch between Karatsuba multiplication and schoolbook long multiplication?
@access private
Definition at line 160 of file BigInteger.php.
◆ MODE_BCMATH
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::MODE_BCMATH = 2 |
To use the BCMath library.
(if enabled; otherwise, the internal implementation will be used)
Definition at line 144 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__construct(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__debugInfo(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_make_odd(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\abs(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_and(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_leftShift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_or(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_rightShift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_xor(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\compare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\divide(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\extendedGCD(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\isPrime(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\multiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\subtract(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toString().
◆ MODE_GMP
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::MODE_GMP = 3 |
To use the GMP library.
(if present; otherwise, either the BCMath or the internal implementation will be used)
Definition at line 150 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__construct(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__debugInfo(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_make_odd(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_normalize(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\abs(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_and(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_leftShift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_or(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_rightShift(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\bitwise_xor(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\compare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\divide(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\equals(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\extendedGCD(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\isPrime(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\modInverse(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\multiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\subtract(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toBytes(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\toString().
◆ MODE_INTERNAL
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::MODE_INTERNAL = 1 |
#-
#+ Mode constants.
@access private
- See also
- BigInteger::__construct() To use the pure-PHP implementation
Definition at line 138 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\__debugInfo().
◆ MONTGOMERY
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::MONTGOMERY = 0 |
#+ Reduction constants
@access private
Definition at line 75 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_reduce().
◆ NONE
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::NONE = 4 |
- See also
- BigInteger::__clone()
Definition at line 91 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_reduce().
◆ POWEROF2
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::POWEROF2 = 2 |
- See also
- BigInteger::_mod2()
Definition at line 83 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_reduce().
◆ SIGN
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::SIGN = 1 |
$result[self::SIGN] contains the sign.
Definition at line 109 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_subtract(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\multiply(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\subtract().
◆ VALUE
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::VALUE = 0 |
#-
#+ Array constants
Rather than create a thousands and thousands of new BigInteger objects in repeated function calls to add() and multiply() or whatever, we'll just work directly on arrays, taking them in as parameters and returning them.
@access private $result[self::VALUE] contains the value.
Definition at line 105 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_barrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsuba(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_karatsubaSquare(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomery(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularBarrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\add(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\multiply(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\subtract().
◆ VARIABLE
| const phpseclib\Math\BigInteger::VARIABLE = 0 |
#-
#+ @access private
- See also
- BigInteger::_montgomery()
- BigInteger::_barrett() Cache constants
$cache[self::VARIABLE] tells us whether or not the cached data is still valid.
Definition at line 122 of file BigInteger.php.
Referenced by phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_barrett(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomery(), phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_montgomeryMultiply(), and phpseclib\Math\BigInteger\_regularBarrett().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- libs/composer/vendor/phpseclib/phpseclib/phpseclib/Math/BigInteger.php